To help you understand the different business data processes that use business intelligence tools, it is important to understand the difference between big data, data mining, and business intelligence. When comparing big data and business intelligence, some people use the term “big data” to refer to the dimensions of the data, while others use the term “big data” to refer to a specific method of analysis. A buzzword used to describe the vast amount of unstructured and structured data that can overwhelm companies day in and day out.
Big data are large datasets that may contain hidden information or insights that cannot be discovered using traditional methods and tools. Data mining refers to the activity of browsing large datasets to find relevant or related information. Data mining is a sequential process that involves using mathematical methods to identify and uncover hidden patterns and information from large datasets to discover patterns.
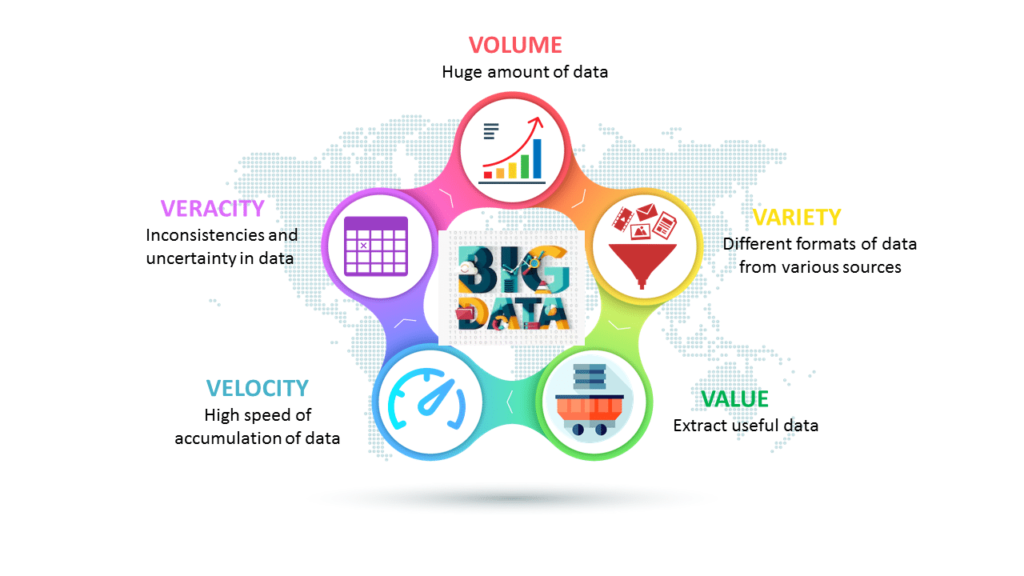
Data mining provides valuable insights by carefully extracting, analyzing, and processing large amounts of data to uncover patterns and relationships that may be important to your business. While data mining is responsible for discovering and extracting patterns and structures in data, data mining uses analytical methods to develop models and test hypotheses. Data analysis leads to the extraction of useful information that can be turned into conclusions, actionable analyses, or recommendations.

Data analysis is the process of extracting, cleansing, transforming, modeling, and visualizing data in order to extract meaningful and useful information that can be useful for summing up and making decisions. Data analysis is the process of analyzing and organizing a set of data in order to explore it in more depth and extract useful information. Data analysis refers to the process of examining sets of information to generate potential hypotheses and conclusions about the data.
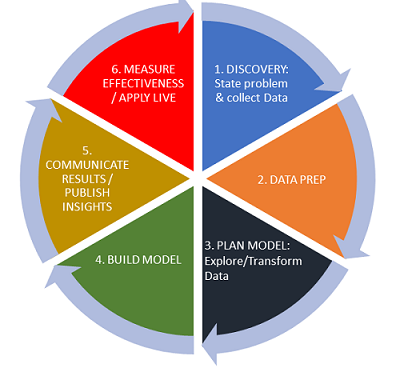
With the right data analysis tools at hand, data scientists can collect, process, and analyze data to make inferences and predictions based on the insights they discover. Data scientists can also use big data analytics to analyze data that may not have been discovered by conventional business programs. The goal of data analyst teams is to work together to uncover information and understand how the data collected can be used to answer questions and solve problems for the business.
Big data refers to the use of large datasets to manage the collection or presentation of data that serve businesses or other recipients. Data mining and big data are two different things, although they both refer to the use of large datasets to manage the data that will serve our purpose, they are two different terms in terms of the operation for which they are used. How huge amounts of information are processed requires an understanding of data mining versus big data—the two phrases are intertwined, but they are not the same.
In short, big data is a resource, and data mining is a processor used to produce useful results. It is not as simple as data mining to complete the functions of big data processing information and business intelligence analysis. On the other hand, big data is very dependent on data mining because we need to find a use for the huge amount of data we have and it is useless without analyzing it.
The volumes of data that can be collected by companies are huge and about big data, but it is necessary to use the data to extract valuable insights, data science. Big data analytics aims at the large volume of datasets, also known as data mining, but data science uses machine learning algorithms to design and develop statistical models to gain knowledge from the big data stack. Data mining is the extraction of vital and valuable information from a huge amount of data. It is a method for tracking and detecting trends in complex datasets. When examining the various stages through which data is “filtered” to make it understandable and usable, big data is the first stage of data collection: it is the point at which the researcher extracts information in its raw form from the source.
Unlike data science pipelines, data mining is more concerned with methods and tools for developing models from previously unknown data and improving the applicability of data for analysis. Data mining is a set of methods and tools widely used by scientists and researchers to extract new and potentially useful information from large, previously unknown datasets and convert it into digestible structures for future use. Data mining involves several target techniques in data processing, but techniques such as pattern recognition, statistical analysis, and data flow recording apply to both. By monitoring the processes involved in data mining and big data, analysts can begin evaluating the data and ultimately make recommendations for improving business processes based on their findings.
After data engineers discover trends and patterns, data scientists analyze (raw) big data using ad hoc techniques (data analysis). After these processes, the models can be viewed as a summary of input data and used in further analysis such as predictive analytics or machine learning. This is currently a key aspect of research and development of strategies to gather meaningful information and insights from available data. Big data is being used by organizations to improve efficiency, understand the untapped market, and increase competitiveness, while data science focuses on providing modeling techniques and techniques to accurately assess the potential of big data.
Data science is a combination of statistics, mathematics, programming, problem-solving, collecting data in raw ways, the ability to see things differently, and the actions of cleaning, preparing, and flattening data. As mentioned earlier, business intelligence is defined as the methods and tools that organizations use to gather insights from data. Inclusion means that business intelligence is not limited to technology – it includes business processes and data analysis programs that facilitate the collection of big data. The job of a data mining expert is to extract the most useful data from it and communicate their findings in a way that the company can understand.